

Similarly, the complementary base pair of the DNA strand 5׳CGT ACG TA3’ cannot be 3׳ U AC AAGGA5’ and 3’ATGTCCTT 5’ as uracil pairs with only adenine and not with cytosine and uracil is an important base of mRNA. The complementary base of 5׳CGT ACG TA3’ cannot be 3׳ T AC AT AGA 5’ as this base pair do not contain the uracil base which must be present because the complementary strand is a mRNA.
Simultaneously, uracil will pair with only one base pair and not more than that. The complementary base cannot be 3׳ UCU AU GAA 5’ on the basis of complementary base pairing because the cytosine always pairs with guanine and it cannot pair with uracil.
Mrna sequence code#
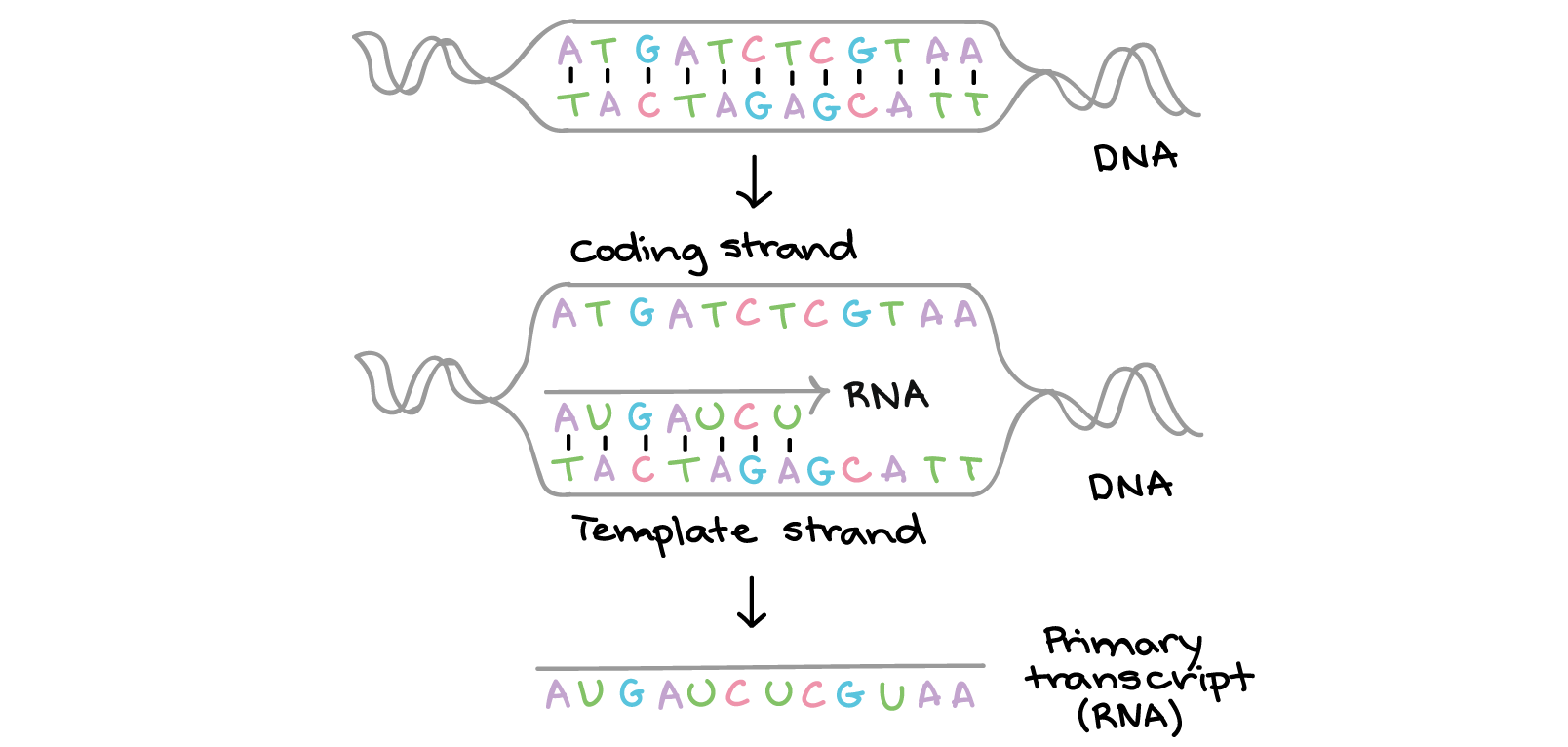
If the DNA sequence has the code as 5׳CGT ACG TA3’ then according to the methods of complementary bases, the bases on the mRNA will read as 3’ GC AUCG AU5’. The information present in the template gene is always read from the 5’ end and moves to the 3’ end. The mRNA carries the encoded information but it is not an identical copy of the DNA molecule. The mRNA is complementary to the template strand but the only difference is the presence of uracil base in place of the thymine base. The information present in the codes carries specific sequences of amino acids within proteins.ĭuring the process of transcription, codes present on the stretch of a DNA which is known as template strand molecules are copied and converted by an RNA molecule known as messenger RNA or mRNA. The nucleic acid sequences carry information in the form of genetic encode. In RNA, uracil is present in place of thymine and it pairs with adenine. In RNA, the base pairs are identical to DNA except for thymine. In the process of pairing, the adenine base pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine. The pairing of the bases takes place due to formation of hydrogen bonds between them. The DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid contains four types of bases which are adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine. Nucleic acids are the most important molecules and the encoded information is transferred through the nucleic acid sequences as it provides an ordering of the base pairs present. The nucleic acids are biopolymers and are composed of a sugar group, a phosphate group and nitrogenous bases. Nucleic acids in living organisms are present in two forms which are DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA or ribonucleic acid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
